Health Wearable Data Security: Privacy and Data Collection Considerations in Smartwatches
2025-05-30

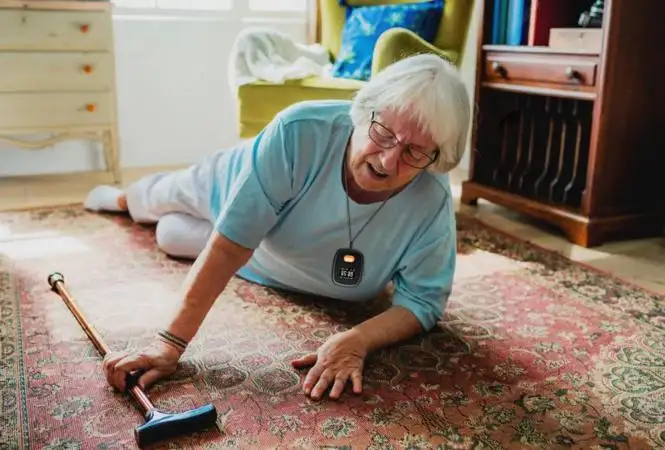
Health smartwatches are now part of everyday life. They help users track steps, heart rate, sleep, and other vital signs. Many people use them to stay active and manage their health. These smartwatches collect private health data. This data includes sensitive information like heart rate and location. As a result, health wearable data security becomes a key concern for all users.
Smartwatches are useful for individuals, but also for businesses. Healthcare providers, elder care facilities, and insurance companies use them to support patients. For them, protecting health data is a legal and ethical responsibility.
Understanding Data Collection in Health Smartwatches
What Data Do Smartwatches Collect?
Smartwatches collect many types of data. These include heart rate, GPS location, sleep patterns, physical activity, and even blood oxygen levels. Some models also detect falls.
How Smartwatches Collect This Data
Health smartwatches use different sensors to gather data. For example, optical sensors track heart rate. Accelerometers measure movement. These tools work together to give a full picture of the user's health.
Short-Term vs Long-Term Monitoring
Some data is used in real time. For example, heart rate alerts may warn of unusual activity. Other data, like sleep trends, is stored and reviewed over time. This helps users and doctors understand health patterns.

How Data Is Transmitted and Stored
How Smartwatches Send Data
After collection, data is sent to paired devices. This usually happens through Bluetooth, Wi-Fi, or cellular networks. It allows users to view their health data on apps or web portals.
Where the Data Goes
Most data is stored in the cloud or on a smartphone. Cloud services allow for long-term storage and access. However, they must follow strict health wearable data security rules to keep information safe.
Protecting Data with Encryption
During transfer and storage, data is often encrypted. This prevents hackers from reading the information if they intercept it. We, as manufacturers, make sure to follow global security standards such as HIPAA and GDPR.

Privacy Risks and Challenges in Health Wearable Data Security
Data Breaches and Unauthorized Access
Smartwatches store sensitive health data. If devices or apps are not secure, hackers can access this data. This is a serious threat to health wearable data security. A single breach can expose private health details to the public.
Misuse of Health Data
Sometimes, companies may use health data for other purposes. This includes advertising, profiling, or sharing with third parties. Users may not be aware of how their data is being used. This reduces trust in the product.
Meeting Global Privacy Rules
Health data is protected by laws like HIPAA in the U.S. and GDPR in Europe. These rules are strict. They require careful handling of health data. As a manufacturer, I must ensure that our devices meet these legal standards. We work hard to follow all privacy laws that apply.
Best Practices for Ensuring Data Privacy
Use of End-to-End Encryption
To keep health data safe, encryption is key. Data should be encrypted before it leaves the device. It should stay encrypted during transfer and storage. This prevents outside access. As a manufacturer, I make sure our smartwatches use strong encryption at all times.
Give Users Control Over Their Data
Users should decide who can see their data. They must be able to turn off data sharing. Clear settings help users manage permissions. This builds trust and supports health wearable data security.
Keep Software Updated and Policies Clear
Security threats change over time. So, firmware and app updates are important. These updates fix bugs and patch security holes. We also make sure our privacy policies are easy to read. Users should understand how we collect and use their data.
Why Privacy and Security Matter to Enterprises
Meeting B2B Compliance Needs
Businesses like hospitals, clinics, and insurers use smartwatches too. They need to protect patient and client data. Health wearable devices must follow rules like HIPAA and GDPR. Health wearable data security is a top concern for these organizations.
Privacy Builds Trust with Business Buyers
Data protection is not just about following laws. It also builds trust. If a business knows our smartwatch protects data, they are more likely to buy it. Strong privacy features can be a reason to choose one product over another.

B2B Benefits of Privacy-Focused Devices
Devices with strong data security offer peace of mind. For elder care or chronic illness monitoring, this is very important. When we design with privacy in mind, our B2B customers can focus on care - not worry about data risks.
Closing Words: Building Trust Through Secure Health Wearables
Health wearable data security is essential for protecting personal and medical information. As smartwatches become more advanced, we must balance innovation with responsible data practices. Strong privacy measures build trust with both users and businesses. Manufacturers, developers, and healthcare partners must work together to prioritize privacy in every stage - from design to deployment.






