The Role of Wearable Monitoring Devices for Elderly in Chronic Disease Management
2025-05-26
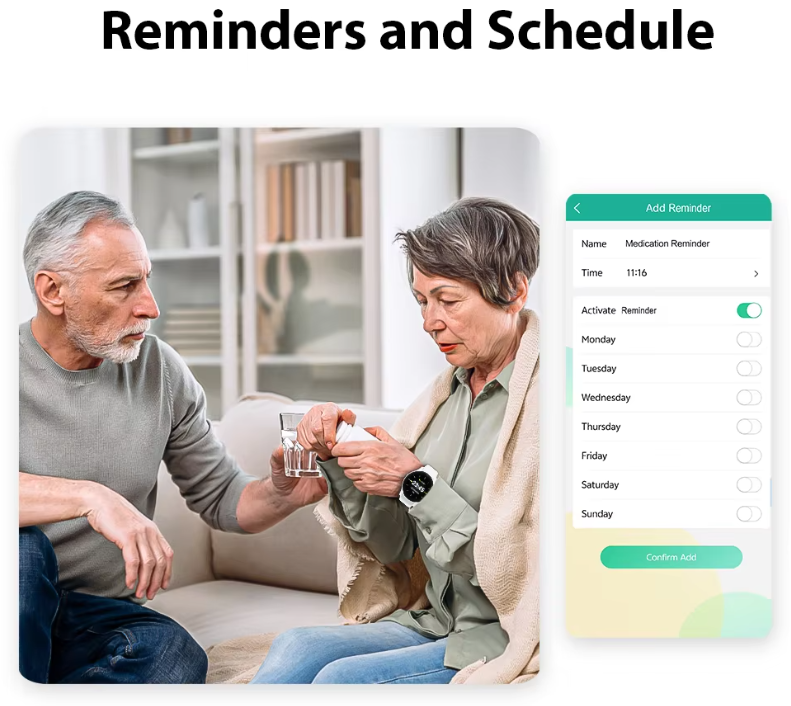
Background: Chronic Disease as a Global Health Crisis
Chronic diseases are a growing public health concern worldwide. They not only severely impact individual well-being but also impose significant financial burdens on families and healthcare systems. According to the World Health Organization, chronic diseases account for 71% of all global deaths – a percentage that continues to rise.

The long-term nature and complexity of these conditions demand consistent self-care and ongoing medical supervision. Patients often need to track vital metrics such as blood pressure and glucose levels, adapting their lifestyle and medications accordingly. Traditional monitoring methods, involving frequent hospital visits and fragmented data collection, are not only inconvenient but also impractical for many elderly patients.
In this context, wearable monitoring devices for elderly patients have emerged as critical tools. These devices offer portability, real-time tracking, and ease of use – transforming how chronic conditions are monitored and managed.
Application of Wearable Monitoring Devices for Elderly in Chronic Disease Management
Real-Time Remote Monitoring
Modern wearable monitoring devices for elderly individuals are equipped with advanced biosensors that continuously track key physiological data such as heart rate, blood pressure, glucose levels, and oxygen saturation. This data is wirelessly transmitted to healthcare providers, allowing them to monitor patients’ health remotely, anytime and anywhere.
For elderly individuals with mobility limitations – such as heart disease patients – these devices reduce the need for in-person visits while ensuring timely access to crucial health data.
Data Logging and Predictive Analysis
These wearable devices go beyond basic tracking. They record daily activities including step count, sleep quality, and exercise levels. This lifestyle data helps doctors understand the correlation between daily habits and chronic conditions.
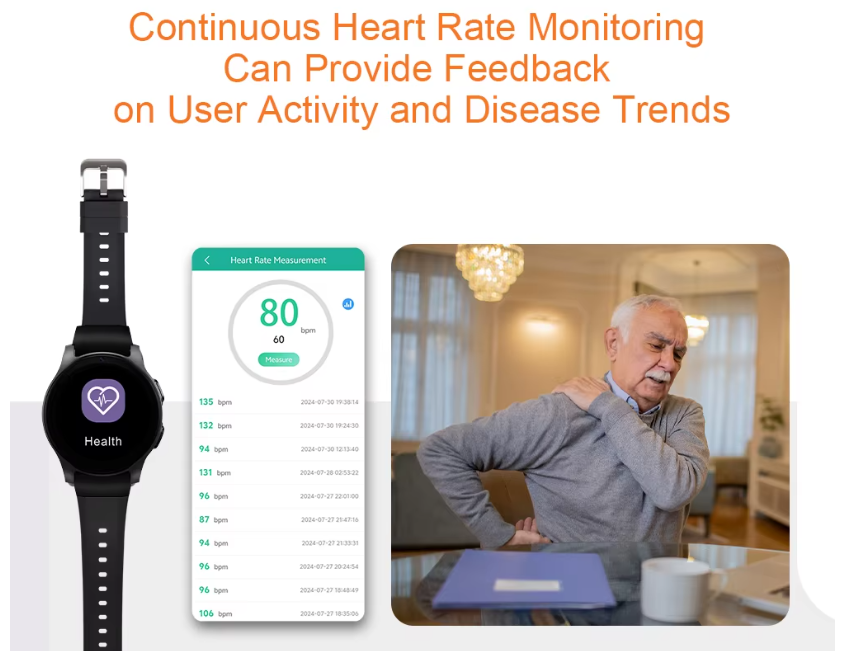
For example, analyzing movement data can reveal if a patient meets physical activity recommendations, enabling customized exercise plans. Sleep tracking can uncover conditions like insomnia or sleep apnea.
Some wearable monitoring devices for elderly come with integrated AI algorithms. These can analyze patterns in heart rate and blood pressure to predict potential cardiac issues or identify deteriorating conditions – empowering doctors to intervene early and adjust treatment accordingly.
Supporting Behavioral Change
Wearable monitoring devices for elderly patients can also serve as behavioral motivators. By setting activity goals and offering real-time feedback, they encourage positive lifestyle changes such as increased movement or healthier eating habits.
Gamified features like challenges or reward systems enhance user engagement. Social functions enable sharing progress with friends or family, fostering accountability and emotional support – especially beneficial for elderly users who may feel isolated.

Challenges in Using Wearable Monitoring Devices for Elderly
Data Privacy and Security
As the volume of sensitive health data grows, protecting user privacy is paramount. Any effective deployment of wearable monitoring devices for elderly users must include stringent data protection protocols to prevent unauthorized access or misuse.
Device Accuracy and Dependability
Measurement accuracy can be affected by external conditions, battery levels, or sensor calibration. For wearable monitoring devices for elderly to be clinically valuable, high reliability and precision are essential.
Battery Life vs. Data Frequency
Chronic disease management often requires frequent data transmission. However, this high-frequency operation rapidly depletes battery life – especially in compact devices designed for elderly users. Since many seniors may find regular charging difficult, this presents a major barrier to consistent use.
Future Development
Technological Advancement and Integration
Future devices will benefit from continued progress in biosensing and AI, enabling even more accurate and comprehensive health monitoring. Integration with electronic medical record (EMR) systems will allow seamless communication between devices and healthcare providers.
Multidisciplinary Collaboration
Effective chronic disease care requires cooperation among various professionals – doctors, nurses, dietitians, and mental health counselors. Wearable monitoring devices for elderly users can serve as shared data hubs that foster coordinated care across disciplines.
Policy Framework and Standardization
Government and regulatory bodies play a key role in supporting adoption. Establishing technical standards and offering policy incentives will ensure safety, reliability, and accessibility of these devices across healthcare settings.
JiAi Intelligent Technology‘s Solution
To address the key challenges in wearable technology, JiAi Intelligent Technology has introduced the L10N health monitoring smartwatch, optimized for elderly users managing chronic diseases. The device utilizes a dual-CPU architecture (4G + BLE): the low-power BLE chip handles real-time data collection and temporarily stores the data, while the 4G chip uploads it in batches – maximizing battery life and reducing the need for frequent charging.
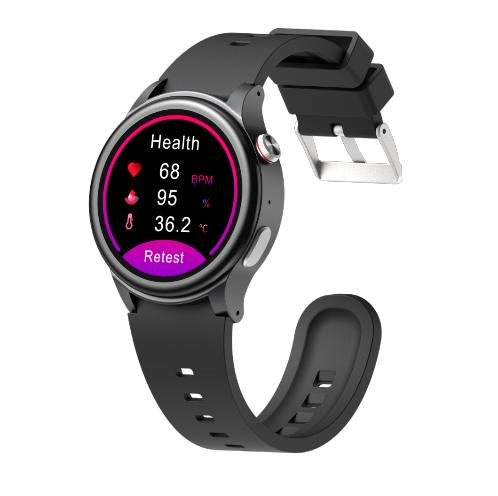

This makes it particularly user-friendly for elderly patients, who may struggle with regular charging routines.
In collaboration with leading medical research institutions across China, JiAi Intelligent Technology has also conducted extensive clinical trials to refine disease prediction models. Backed by a network of over 1,000 B2B clients, the company continuously updates its cloud-based AI algorithms. By combining robust hardware and intelligent analytics, JiAi Intelligent Technology offers a complete solution for managing chronic conditions through wearable monitoring devices for elderly users.






